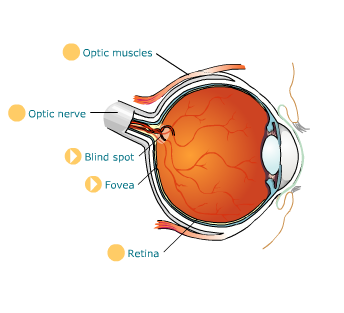
The retina
The retina lines the rear of the interior of the eye. It contains two kinds of light-sensitive cells:
- rods – which can function in dim light but do not recognise colour
- cones – which are responsible for colour vision.
Impulses from the rods and cones are transmitted along nerve fibres that converge to form the optic nerve. This conveys the signals to the brain where they are interpreted at the occipital lobe.
At the centre of the retina is the fovea (also known as the macula lutea ). This part of the retina only has cone cells and can resolve very fine detail.
Next we'll look at the optic muscles that control movement of the eye.
